Definition
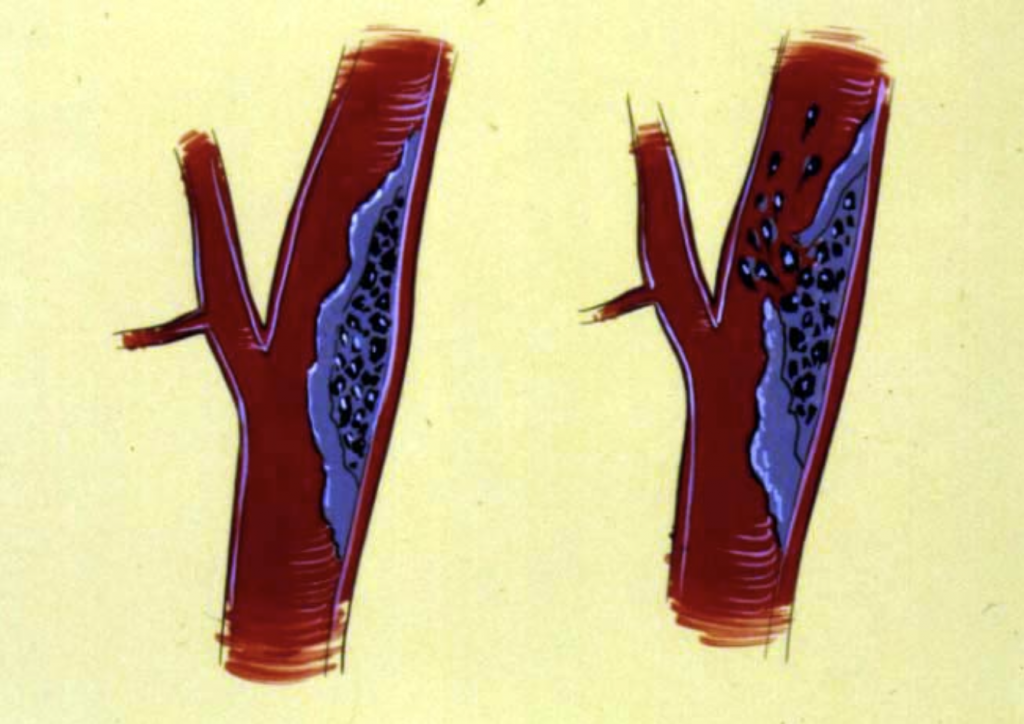
Vascular and endovascular surgeons deal with carotid artery disease specifically in trying to prevent stroke. The arterial lesion at the carotid bifurcation in the neck is usually one of atherosclerosis. Dissection is another possible pathology but it is less commonly seen.
Patients may present with an asymptomatic lesion that is incidentally discovered during examination clinically or with ultrasound. Another common presentation is one of stroke or mini stroke on the side of the lesion that is present at the carotid bifurcation. This usually presents as a lateralizing symptom or sign.
There may be transient monocular blindness (amaurosis fugax), weakness down one side of the body, or loss of speech or drooping of the face. If these events recover within 24 hours then they are called TIA’s (transient ischemic attacks) and if not they are often referred to as a stroke.
Fig 1. Arterial lesion of the carotid artery.
Treatment
Patients presenting with these symptoms or signs require clinical examination and a duplex ultrasound scan to determine the degree of atheromatous plaque at the carotid bifurcation to see if they would be suitable for carotid endarterectomy to protect them from a stroke in the future.
Risks of Carotid Surgery
The risks associated with carotid surgery include myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke or mini-stroke during surgery or soon after, bleeding and infection as with any surgery.
There are nerves that are close by in the operating field and patients can awake with a croaky voice or a funny tongue or a flattened lower lip and these will usually recover quickly.
Patients may have numbness under the chin at the site of the incision and occasionally will get some numbness on the ear lobe that can be transient. This may be annoying for females who wear earrings and for males who shave.
If you would like to discuss your symptoms with Dr Campbell

